Top 5 Fusion Protein Applications Changing the Medical Field
Medical science benefits from five revolutionary fusion protein applications which include cancer treatment and drug delivery systems and additional advancements.
Introduction
Healthcare progresses through revolutionary innovation because fusion proteins create solutions to medical problems that are difficult to tackle. The targeting precision of two or more protein parts in bioengineered molecules exceeds traditional medical interventions to treat diseases effectively.
The basis of present-day medical progress rests on fusion proteins because these proteins transform healthcare practices for diagnosis and treatment and disease prevention methods. The specific protein structure enables detailed functions that enable researchers to target cancer cells accurately while maintaining protection of regular tissues and delivering genetic material to cells. The healthcare industry alongside biotechnology sector experiences revolutionary transformation through this innovative technology.
We investigate the main medical purposes of fusion proteins using performance evaluations as we examine upcoming therapeutic breakthroughs.
What Are Fusion Proteins?
Essential protein functions combine as fusion proteins to form unified chemical compounds. A single fusion protein can unite various domains from unique purposes to create outcomes that would not be possible when using the domains independently.
Manufacturing these proteins demands the use of recombinant DNA technology to combine genetic material from diverse sources at host cells to produce the proteins. Through recombinant DNA technology scientists obtain proteins at large quantities that serve medical diagnostics as well as therapeutic treatments.
Key Benefits of Fusion Proteins
- The specific targeting ability leads to reduced occurrence of unintended target effects.
- The engineered tool shows flexibility because it serves both cellular targeting systems and immune system modification methods.
- Effective Delivery: Ideal for precision treatments like gene therapy or cancer immunotherapy.
Explore the fundamentals of fusion protein technology and how it’s shaping modern medicine.
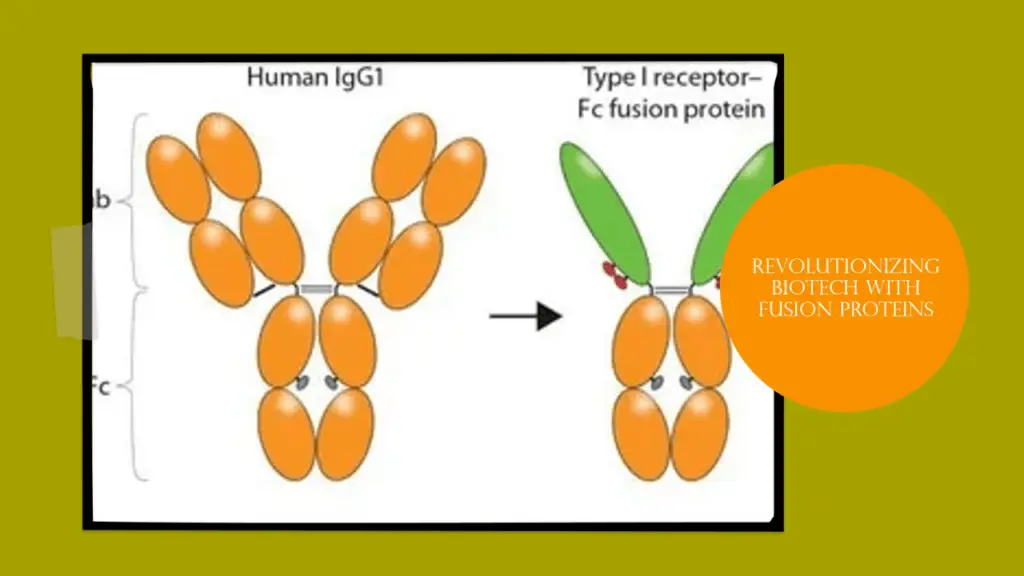
Top 5 Applications in Medicine
Medical practices demonstrated transformational changes because of fusion protein applications within fields. The main operational effects of fusion proteins emerge within these specific domains.
1. Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer treatments are being revolutionized by fusion proteins, which are integral to modern immunotherapy approaches.
- Checkpoint Blockade Therapy
Checkpoint inhibitors known as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blocking antitumor agents function as fusion proteins to help immune cells recognize and fight cancer cells. Cancer cells cannot shield the immune response thus allowing these treatments to trigger T-cell assault against tumors. - Bispecific T-cell Engagers (BiTEs)
The novel fusion proteins act as connectors to join T-cells with cancer cells which allows the directed immune response to eradicate tumors. Fusion proteins produce a concentrated and powerful elimination of cancer tissue.
Impact: New therapy approaches relying on fusion proteins result in significant improvements of cancer survival outcomes within melanoma and lung cancer patients while providing hope to patients facing late-stage diseases.
2. Targeted Drug Delivery
Fusion proteins excel in targeted drug delivery, offering a safer way to treat conditions such as cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders.
- Fusion proteins enable therapeutic molecule delivery to disease cells without affecting healthy tissues in the human body.
- Example: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) utilize fusion proteins to carry potent drugs directly to cancer cells, minimizing systemic side effects.
Impact: Patients receive less adverse effects through targeted delivery systems which produce improved therapeutic outcomes particularly in antiviral and chemotherapy treatments.
People should study the advantages that fusion proteins bring to precise drug delivery systems.
3. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy executions need specific cellular material delivery capabilities because fusion proteins serve as critical transportation elements.
- Cells accept therapeutic genes through the combination of viral vectors and fusion proteins which provide them entry access. Cell structures allow therapeutic genes to serve medical functions including fixing genetic problems or creating proteins used for genetic disorder treatment.
- Applications: Various fusion protein-based gene delivery systems manage conditions such as hemophilia and spinal muscular atrophy and other rare medical cases.
Impact: Through this method healthcare practitioners establish long-term treatments for patients who were previously considered untreatable because of genetic diseases.
4. Autoimmune Disease Treatment
Fusion proteins are also being used to treat autoimmune diseases by modulating immune system activity.
- Example: Through its Etanercept (Enbrel) treatment the production of inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha gets blocked to support patients managing rheumatoid arthritis as well as psoriasis conditions..
- These therapies reduce systemic inflammation, providing relief from pain and halting disease progression.
Impact: People experience better physical movement ability and reduced inflammation frequency together with major life improvements.
5. Diagnostic and Imaging Tools
The versatility of fusion protein technology extends beyond treatment into diagnostics.
- Fusion Tags for Imaging: Proteins combined with fluorescent or radiolabeled markers enable researchers and clinicians to track biological processes and detect disease at early stages.
- Applications: These tools are invaluable in imaging tumors, assessing disease progression, and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Impact: The utility of diagnostic fusion proteins for identifying diseases leads to improved illness management and early intervention between research applications and clinical treatments.
FAQs About Fusion Proteins
1. What are the benefits of fusion proteins in medicine?
The amalgamation of proteins into fusion proteins allows precise drug delivery systems that decrease negative effects while achieving multiple objectives which supports their use in therapeutic applications and genetics fields.
2. How are fusion proteins used in diagnostics?
By attaching diagnostic markers such as fluorescent proteins, fusion proteins help detect diseases, monitor progression, and visualize cellular processes in real time.
3. Are fusion protein treatments safe?
Most therapeutic fusion protein treatments pass through rigorous clinical testing before approval for safety and effectiveness purposes. The risks of side effects are reasonable when compared to therapy advantages.
4. Can fusion proteins treat rare diseases?
Absolutely. By enabling targeted treatments or gene corrections, fusion proteins are particularly effective in addressing rare or genetic conditions.
5. What makes fusion proteins unique compared to traditional therapies?
Unlike traditional therapies, fusion proteins combine multiple functionalities in one molecule, offering unmatched precision and therapeutic benefits.
Call to Action
Research on fusion proteins leads directly to progressive medical breakthroughs that work for cancer therapy and gene therapy applications and additional medical developments. Bioengineered molecules serve as medical breakthroughs to eliminate darkness in conditions with no alternatives.
